Advancing Sustainable Concrete Through Rigorous Evaluation
The Lab2Slab program, led by UC Pavement Research Center (UCPRC) and UC Davis Materials Decarbonization and Sustainability Center (MDSC), applies a structured, step-wise, risk-based approach to evaluating supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) and sustainable cements and moving them to practice by addressing the key risks for concrete producers, designers, and procurers in a timely and cost-effective manner.The goal is to generate high-quality, performance-based data that supports the widespread adoption of sustainable concrete in infrastructure projects.
By combining laboratory research, pilot-scale testing, and full-scale implementation, Lab2Slab provides a clear pathway from material innovation to real-world application while addressing barriers to adoption that can slow down industry-wide implementation.
The Lab2Slab Framework: A Hierarchical Approach
Lab2Slab follows a stepwise evaluation process that progresses materials through increasing scales of production from controlled laboratory conditions to full-scale infrastructure implementation, providing risk assessment data from testing and construction at each step. By combining laboratory research, pilot-scale testing, and full-scale implementation, Lab2Slab provides a clear pathway from material innovation to real-world application while addressing barriers to adoption that can slow down industry-wide implementation. The step-wise approach ensures technical performance, constructability, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact are all validated before widespread use. It provides feedback information to new materials suppliers at each stage to improve their product at each scale of production, reducing their costs and risks of going to a large field pilot project before they are ready.
Production Scale and Testing Stages
Materials are evaluated through a four-stage hierarchical testing framework:
- Lab Scale (TRL 3-4) – Bench-scale testing under controlled conditions, first mortar scale and then concrete scale using 1 kg then 10 kg
- Lab2Slab Scale (TRL 5-6) – Pilot-scale testing with small batch material production (1-2 tons)
- Slab2Pilot Scale (TRL 7-8) – Full-scale test sections using 10s to 100s of tons of material
- Pilot2Practice Scale (TRL 9) – Widespread adoption and integration into standard practice
This approach reduces uncertainty and bridges the gap between research and real-world implementation—a gap often referred to as the Valley of Death, where many promising materials fail to reach commercialization.

Key Evaluation Metrics
To support successful adoption, each material undergoes comprehensive testing based on five critical factors, with increasing details at each step:
- Engineering strength and durability – Compressive strength, flexural strength, shrinkage, and long-term durability testing
- Scalability and production feasibility – Regional availability of raw materials, supply chain considerations, and large-scale production feasibility
- Constructability – Workability, setting times, finishing characteristics, and compatibility with standard construction practices
- Cost and lifecycle analysis – Material costs, long-term maintenance needs, and life-cycle cost analysis compared to traditional concrete
- Environmental impact – Reduction in embodied carbon, energy intensity, and potential to use industrial byproducts or alternative materials
Addressing Adoption Barriers
Adoption of sustainable concrete faces several challenges that Lab2Slab seeks to mitigate:
- Economic concerns – Cost differentials between new materials and traditional cement alternatives can slow adoption.
- Specification development and standard specifications must evolve to accommodate sustainable materials.
- Permitting – Permitting
- Supply chain and logistics – Ensuring raw material availability and transportation networks is crucial.
- Construction compatibility – Workability, curing times, and compatibility with existing admixtures impact industry adoption.
- Lack of data and demonstration projects – Clear, public performance data is necessary to build concrete producer and procurer confidence.
Lab2Slab provides structured risk assessment tools that address these barriers at each stage of the evaluation process.
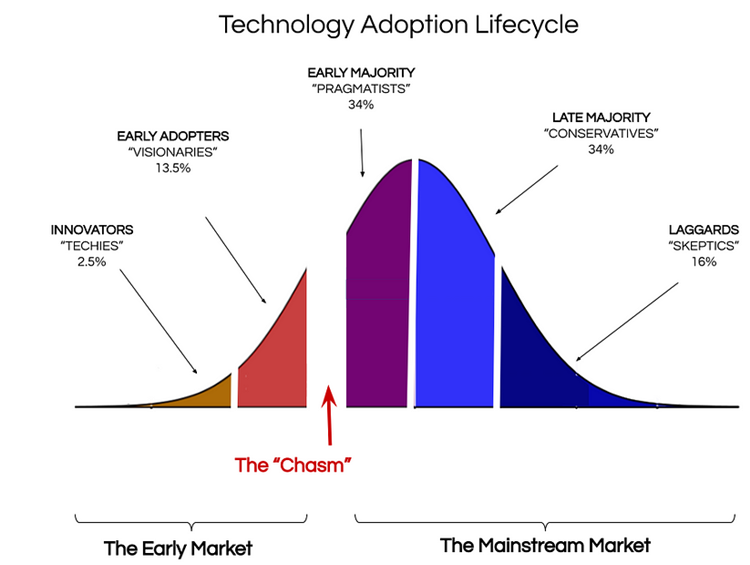
Technology Adoption Life Cycle
The Lab2Slab framework helps bridge “the Chasm” in the well-known Technology Adoption Life Cycle by recognizing that new materials need risk assessment as they progress from research to pilot testing, full-scale implementation, and eventually standard practice. Lab2Slab strategically supports each stage by addressing risks, providing open-access performance data in a comprehensive standardized format, and later in the process developing specifications and other practice documents needed for implementation.
Data Transparency & Knowledge Sharing
-
Lab2Slab is committed to open-access data sharing to support widespread adoption of sustainable concrete technologies. Performance data, material evaluations, and life-cycle assessments will be made available to:
- Researchers and academics – To advance scientific understanding and further material development
- Contractors and concrete purchasers – To provide performance data that informs real-world application
- Government agencies and policymakers – To support the integration of sustainable concrete into infrastructure codes, specifications, and procurement policies
Learn More
For additional details on ongoing material evaluations, test track projects, and research findings, visit:
